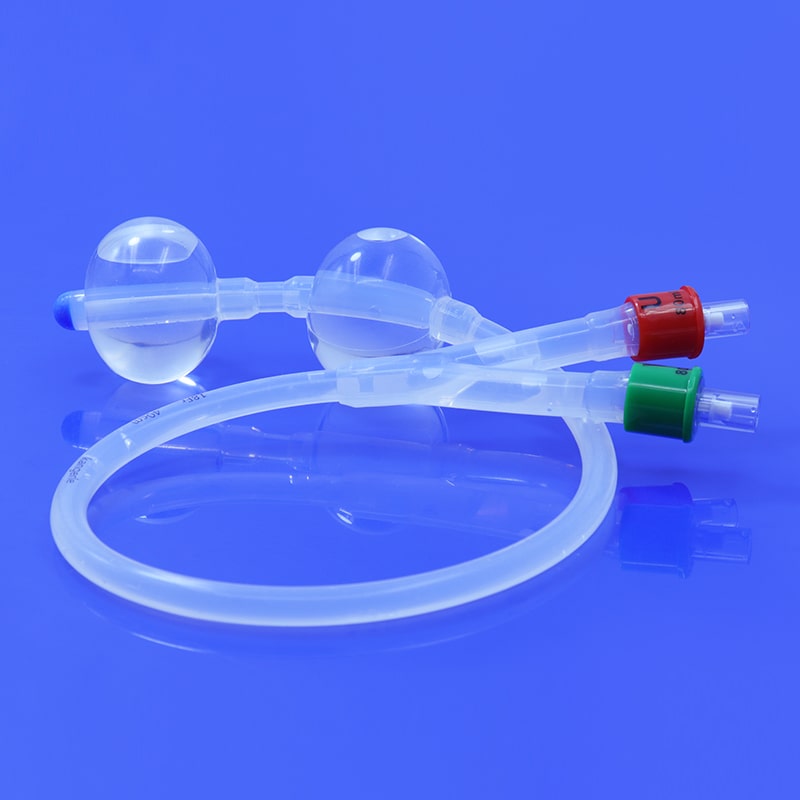
Hysterosalpingography Catheter: A Comprehensive Guide

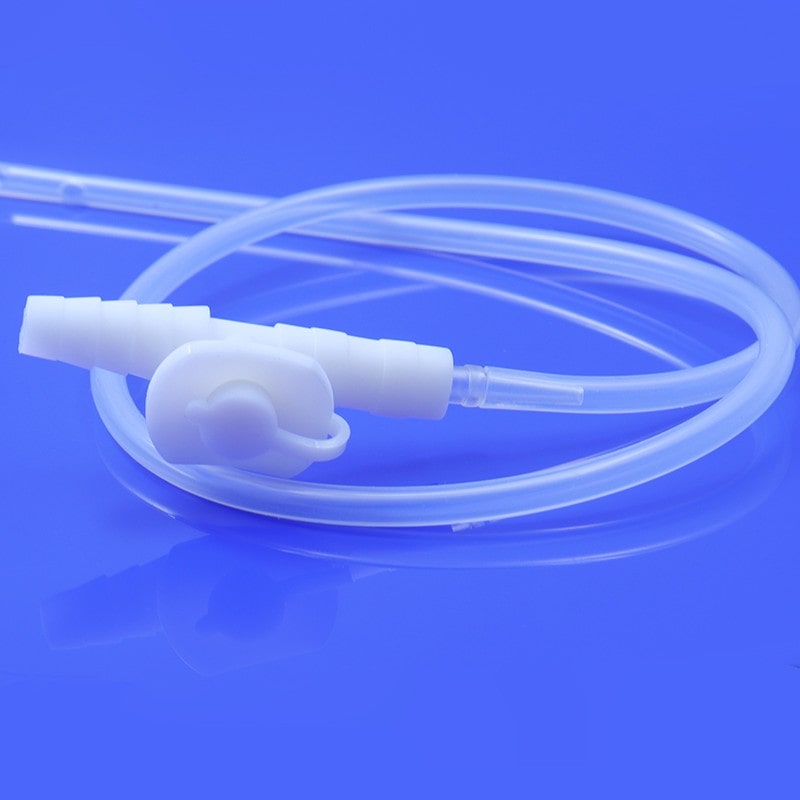
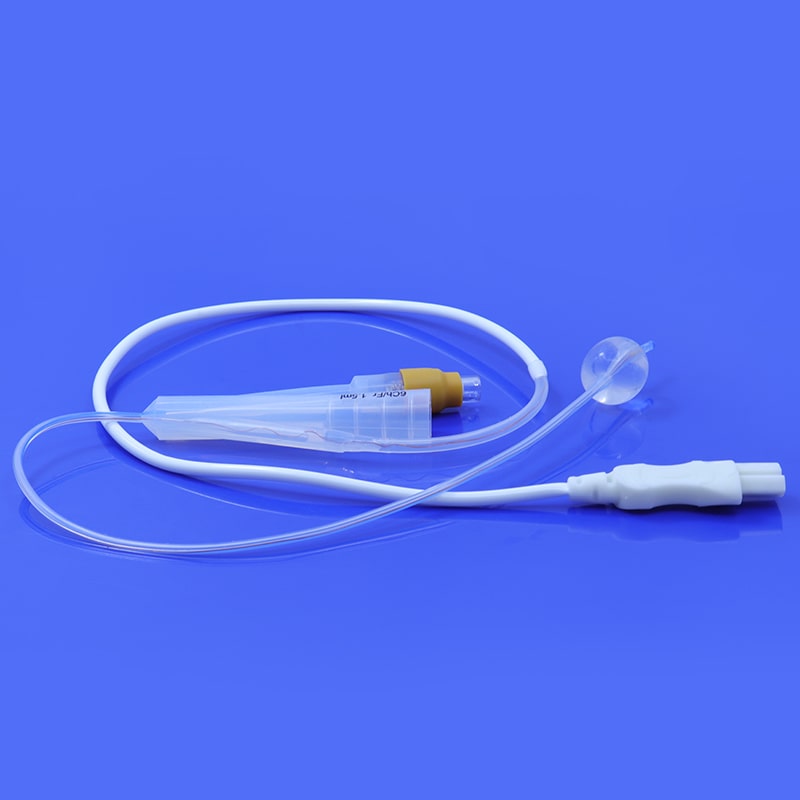
HSG Catheter is a flexible medical tube made of silicone material, it is often used to evaluate the health and functionality of a woman's uterus and fallopian tubes. The HSG catheter is an integral component of the hysterosalpingography procedure. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to understanding the HSG catheter, its use, the procedure, and its significance in reproductive health.
What is an HSG Catheter?
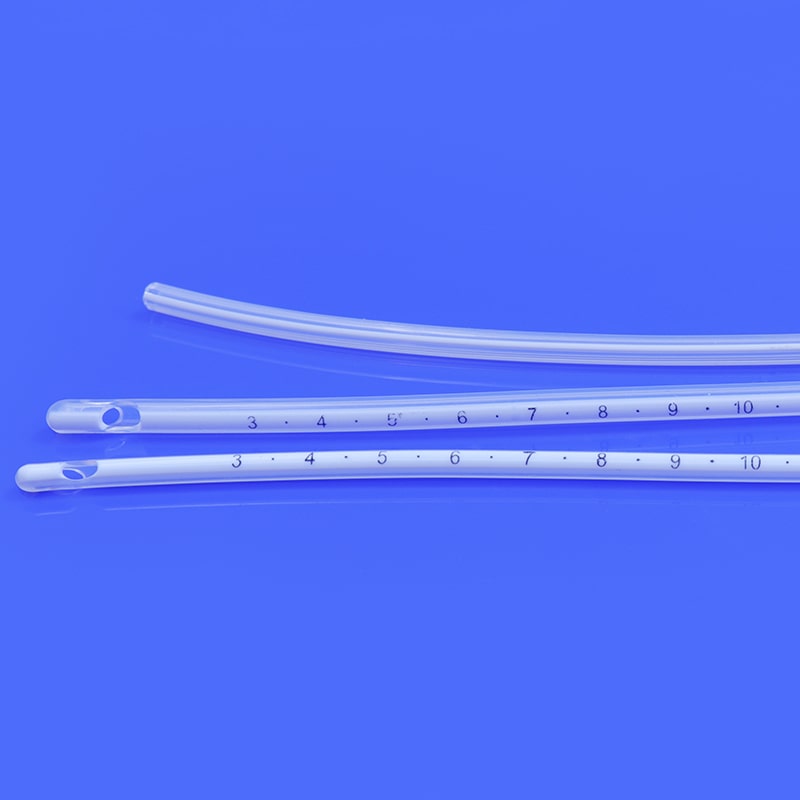
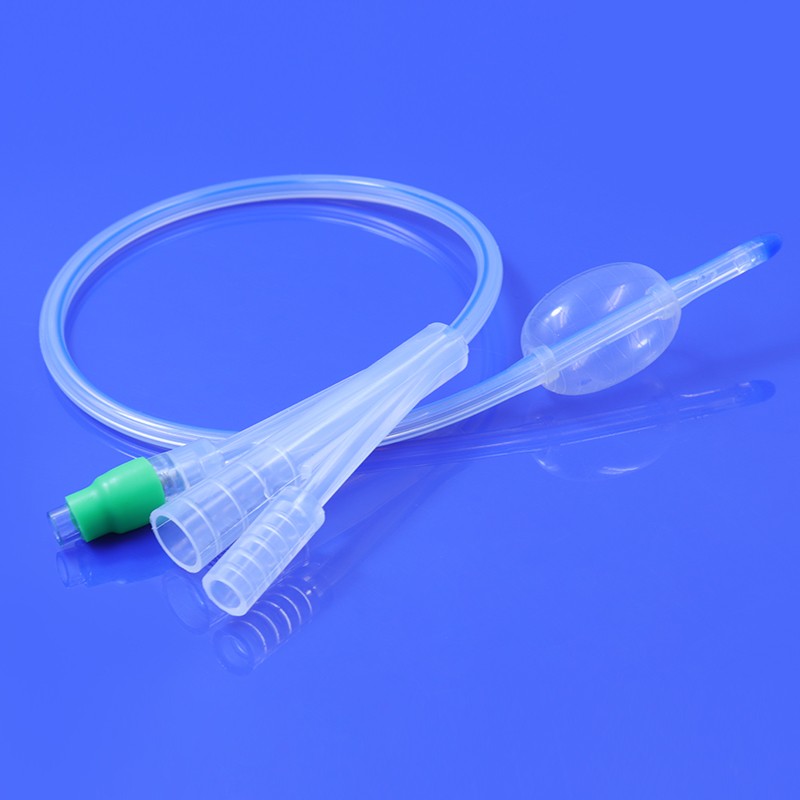
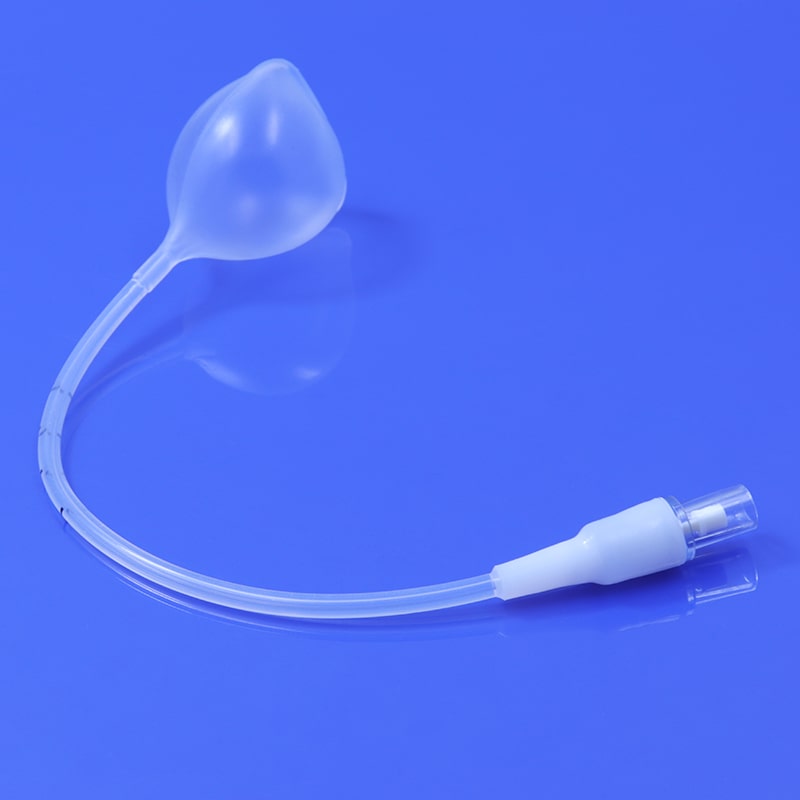
A HSG catheter, or hysterosalpingography catheter, is a thin, flexible tube designed for introducing contrast material into the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes during an HSG procedure. This catheter allows for the visualization of the reproductive organs through X-ray imaging, helping healthcare professionals identify potential issues such as blockages, abnormalities, or structural problems.
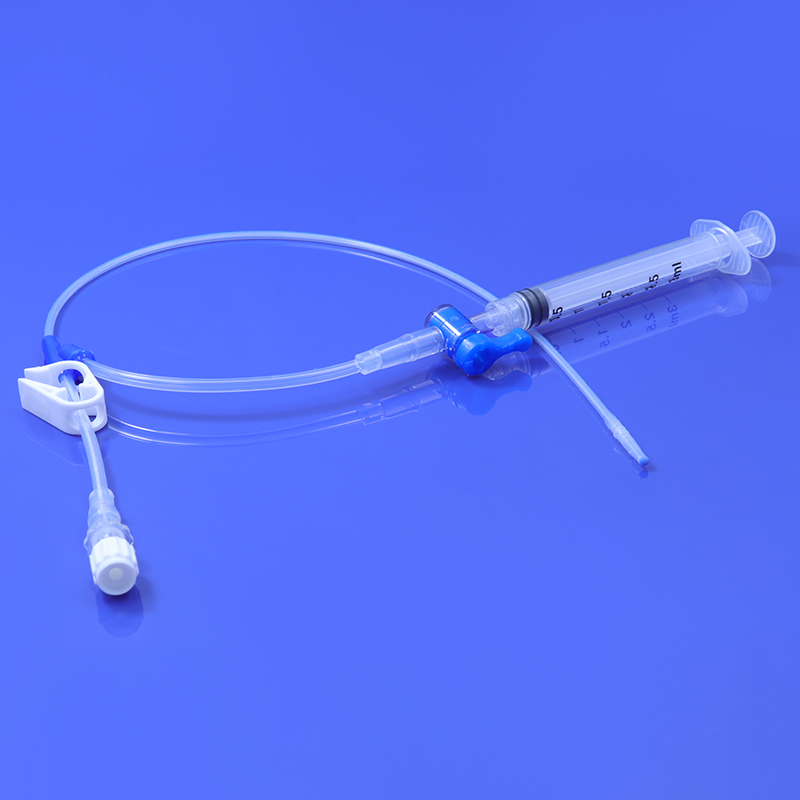
Uses of HSG Catheter
The primary purpose of the HSG catheter is to facilitate the injection of contrast material into the reproductive system, allowing radiologists to capture detailed X-ray images. The contrast material helps highlight the contours and structures of the uterus and fallopian tubes, making it easier to detect any abnormalities that may affect fertility.
Instruction of how to use HSG catheter
Preparation: Before the HSG procedure, patients may be advised to take pain relievers or mild sedatives to alleviate potential discomfort.
Positioning: The patient is positioned on an X-ray table, typically in a lithotomy position, similar to a pelvic exam.
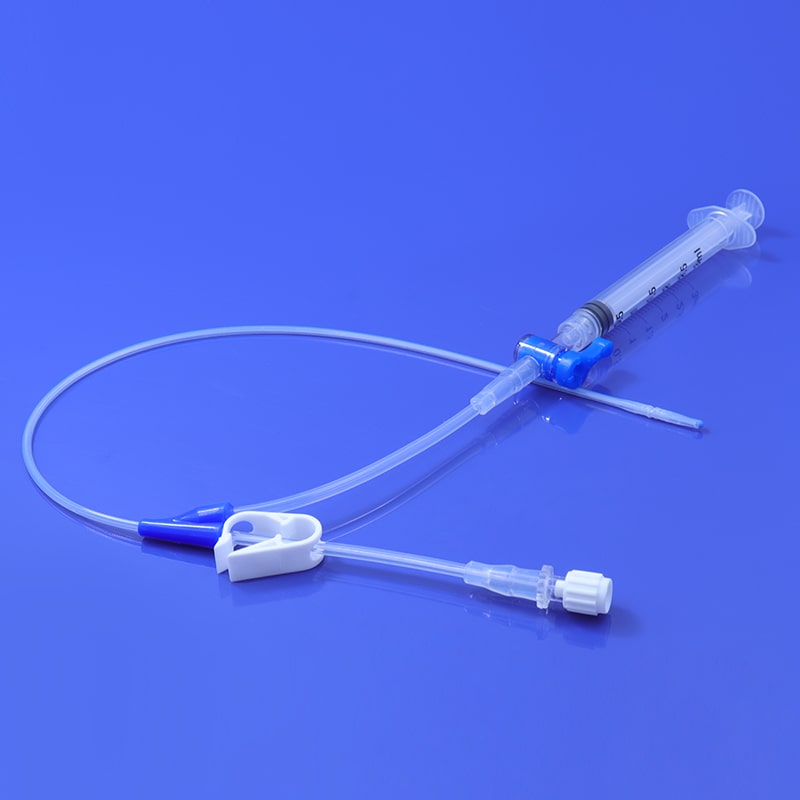
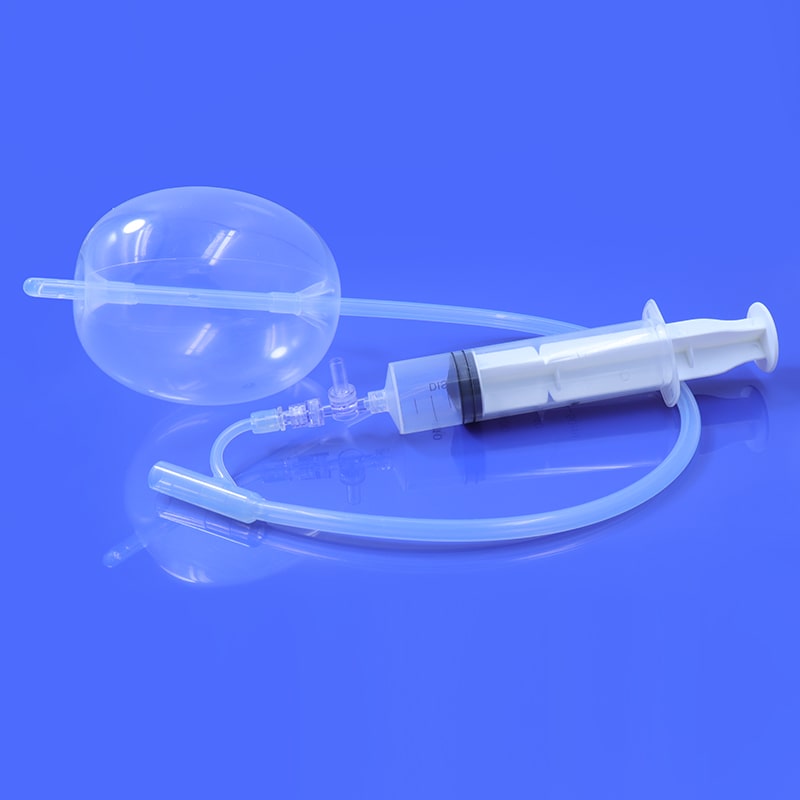
Catheter Insertion: The HSG catheter is carefully inserted into the cervix and guided into the uterine cavity. This process is performed under sterile conditions to minimize the risk of infection.
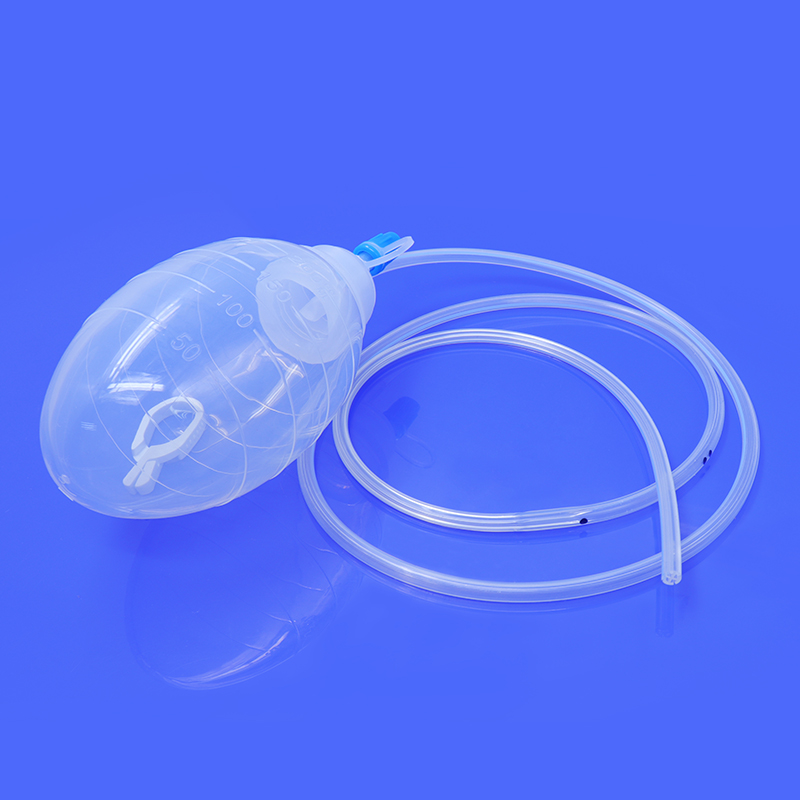
Contrast Injection: Once the catheter is in place, a radiopaque contrast material is injected through the catheter into the uterus. The contrast material flows through the uterus and into the fallopian tubes, highlighting their shape and structure.
X-ray Imaging: As the contrast material moves through the reproductive organs, X-ray images are captured in real-time. These images help healthcare professionals assess the uterine cavity, the patency of the fallopian tubes, and the presence of any abnormalities.
Post-Procedure: After the procedure, patients may experience mild cramping or discomfort, but these symptoms typically subside shortly after completion. Some women might also notice a temporary increase in fertility following the HSG.
Share this product to: